10.10.13.208/29 is correct
Topic 1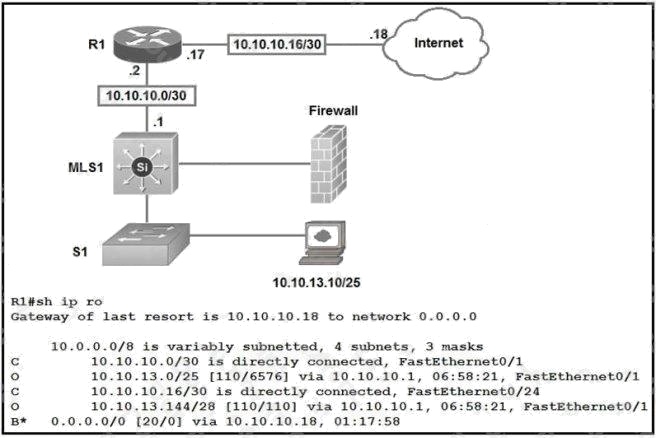
Refer to the exhibit. Which type of route does R1 use to reach host 10.10.13.10/32?
B
Topic 1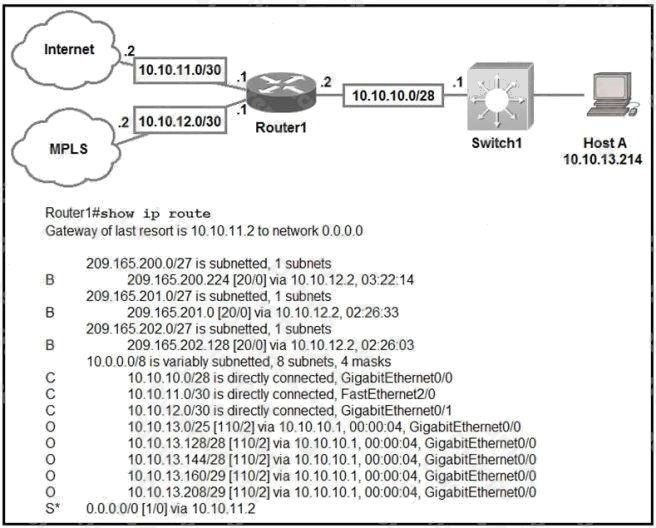
Refer to the exhibit. Which prefix does Router1 use for traffic to Host A?
D
Explanation:
The prefix with longest prefix will be matched first, in this case is /29.
10.10.13.208/29 is correct
10.10.13.208
C 10.10.13.144/28
10.10.13.208/29 is correct
D longest match
Topic 1
DRAG DROP
Drag and drop the descriptions of file-transfer protocols from the left onto the correct protocols on the right.
Select and Place: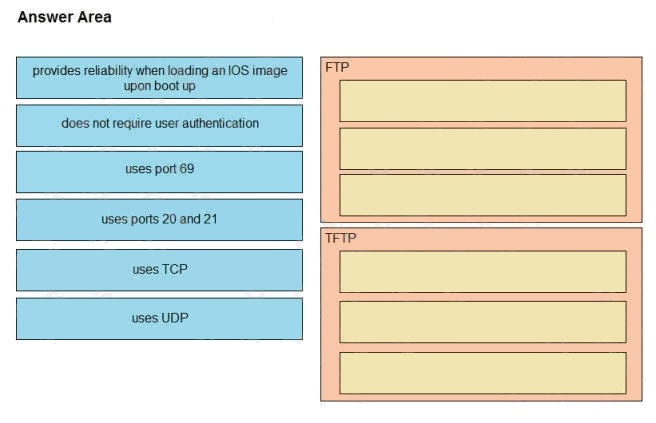
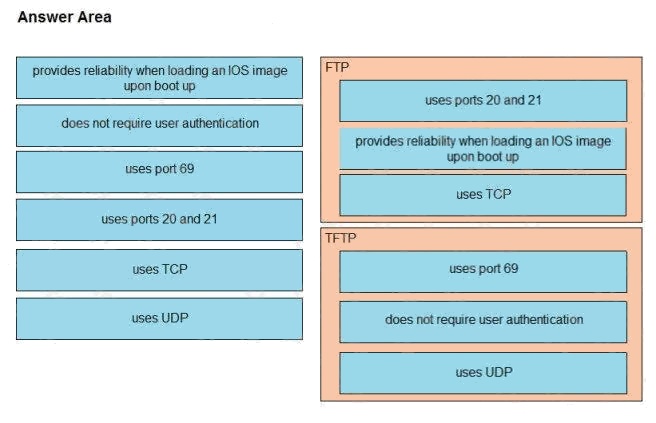
Correct ,
TFTP is not secure
Provide rliability - TCP
doesnot require user - TFTP
uses port 69 - TFTP
Port 20-21 -FTP
User TCP - FTP
uses UDP - TFTP
Topic 1
A frame that enters a switch fails the Frame Check Sequence. Which two interface counters are incremented? (Choose two.)
A D
Explanation:
Whenever the physical transmission has problems, the receiving device might receive a frame whose bits have changed
values. These frames do not pass the error detection logic as implemented in the FCS field in the Ethernet trailer. The
receiving device discards the frame and counts it as some kind of input error. Cisco switches list this error as a CRC error.
Cyclic redundancy check (CRC) is a term related to how the FCS math detects an error.
The input errors includes runts, giants, no buffer, CRC, frame, overrun, and ignored counts.
The output below show the interface counters with the show interface s0/0/0 command: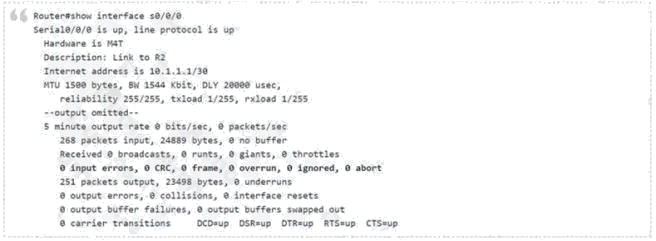
ANS is correct AD
AD are correct
Topic 1
DRAG DROP
Drag and drop the IPv4 network subnets from the left onto the correct usable host ranges on the right.
Select and Place: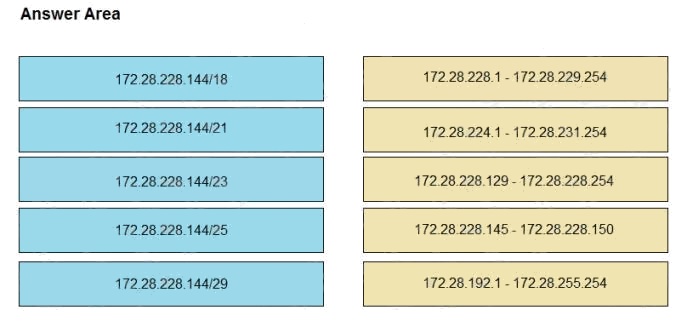

Explanation:
This subnet question requires us to grasp how to subnet very well. To quickly find out the subnet range, we have to find out
the increment and the network address of each subnet. Lets take an example with the subnet 172.28.228.144/18:
From the /18 (= 1100 0000 in the 3rd octet), we find out the increment is 64. Therefore the network address of this subnet
must be the greatest multiple of the increment but not greater than the value in the 3rd octet (228). We can find out the 3rd
octet of the network address is 192 (because 192 = 64 * 3 and 192 < 228) -> The network address is 172.28.192.0. So the
first usable host should be 172.28.192.1 and it matches with the 5th answer on the right. In this case we dont need to
calculate the broadcast address because we found the correct answer.
Lets take another example with subnet 172.28.228.144/23 -> The increment is 2 (as /23 = 1111 1110 in 3rd octet) -> The
3rd octet of the network address is 228 (because 228 is the multiply of 2 and equal to the 3rd octet) -> The network address
is 172.28.228.0 -> The first usable host is 172.28.228.1. It is not necessary but if we want to find out the broadcast address
of this subnet, we can find out the next network address, which is 172.28.(228 + the increment number).0 or 172.28.230.0
then reduce 1 bit -> 172.28.229.255 is the broadcast address of our subnet. Therefore the last usable host is
172.28.229.254.
ANS is Correct
Topic 1
How do TCP and UDP differ in the way that they establish a connection between two endpoints?
A
A is the correct answer
A is correct ans
Topic 1
Which 802.11 frame type is Association Response?
A
Explanation:
There are three main types of 802.11 frames: the Data Frame, the Management Frame and the Control Frame. Association
Response belongs to Management Frame. Association response is sent in response to an association request.
Reference: https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/802.11_Frame_Types
A is the correct answer
A. Management
Topic 1
In which way does a spine-and-leaf architecture allow for scalability in a network when additional access ports are required?
C
Explanation:
Spine-leaf architecture is typically deployed as two layers: spines (such as an aggregation layer), and leaves (such as an
access layer). Spine-leaf topologies provide high-bandwidth, low-latency, nonblocking server-to-server connectivity.
Leaf (aggregation) switches are what provide devices access to the fabric (the network of spine and leaf switches) and are
typically deployed at the top of the rack. Generally, devices connect to the leaf switches. Devices can include servers, Layer
4-7 services (firewalls and load balancers), and WAN or Internet routers. Leaf switches do not connect to other leaf switches.
In spine-and-leaf architecture, every leaf should connect to every spine in a full mesh.
Spine (aggregation) switches are used to connect to all leaf switches and are typically deployed at the end or middle of the
row. Spine switches do not connect to other spine switches.
Reference: https://www.cisco.com/c/en/us/products/collateral/switches/nexus-9000-series-switches/guide-c07-733228.html
Correct
When you add new leaf switch it automatically gains connections to every other spine switch
C is correct
Topic 1
Which statement identifies the functionality of virtual machines?
C
C is the correct Answer
C is correct
Topic 1
Which command automatically generates an IPv6 address from a specified IPv6 prefix and MAC address of an interface?
C
Explanation:
The ipv6 address autoconfig command causes the device to perform IPv6 stateless address auto-configuration to discover
prefixes on the link and then to add the EUI-64 based addresses to the interface. Addresses are configured depending on
the prefixes received in Router Advertisement (RA) messages. The device will listen for RA messages which are transmitted
periodically from the router (DHCP Server). This RA message allows a host to create a global IPv6 address from:
Its interface identifier (EUI-64 address)
Link Prefix (obtained via RA)
Note: Global address is the combination of Link Prefix and EUI-64 address
C is correct
Topic 1
When configuring IPv6 on an interface, which two IPv6 multicast groups are joined? (Choose two.)
D E
Explanation:
When an interface is configured with IPv6 address, it automatically joins the all nodes (FF02::1) and solicited-node
(FF02::1:FFxx:xxxx) multicast groups. The all-node group is used to communicate with all interfaces on the local link, and the
solicited-nodes multicast group is required for link-layer address resolution. Routers also join a third multicast group, the all-
routers group (FF02::2).
Reference:
https://www.cisco.com/c/en/us/td/docs/ios-xml/ios/ipv6/configuration/xe-3s/ipv6-xe-36s-book/ip6-multicast.html
DE are correct
Topic 1
DRAG DROP
Refer to the exhibit. Drag and drop the networking parameters from the left onto the correct values on the right.
Select and Place:
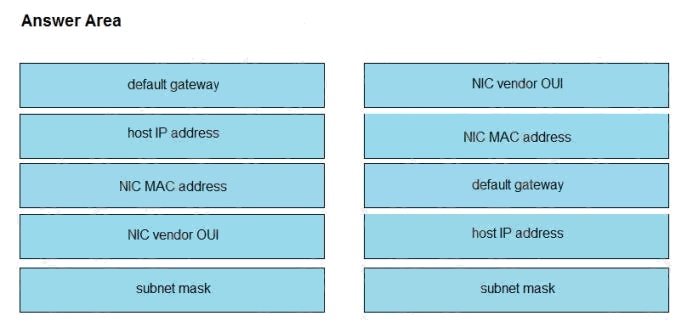
Explanation:
The ip route and ip addr show eth1 are Linux commands.
ip route: display the routing table
ip addr show eth1: get depth information (only on eth1 interface) about your network interfaces like IP Address, MAC
Address information
Topic 1
What is the default behavior of a Layer 2 switch when a frame with an unknown destination MAC address is received?
C
Explanation:
If the destination MAC address is not in the CAM table (unknown destination MAC address), the switch sends the frame out
all other ports that are in the same VLAN as the received frame. This is called flooding. It does not flood the frame out the
same port on which the frame was received.
C it floods the packets to all ports
Topic 1
An engineer must configure a /30 subnet between two routes. Which usable IP address and subnet mask combination meets
this criteria?
D
D is correct
Topic 1
Which network allows devices to communicate without the need to access the Internet?
B
Explanation:
This question asks about the private ranges of IPv4 addresses. The private ranges of each class of IPv4 are listed below:
Class A private IP address ranges from 10.0.0.0 to 10.255.255.255
Class B private IP address ranges from 172.16.0.0 to 172.31.255.255
Class C private IP address ranges from 192.168.0.0 to 192.168.255.255
Only the network 172.28.0.0/16 belongs to the private IP address (of class B).
B is correct
B is one of the OSPF routes so this should be correct
host route
B is one of the OSPF routes so this should be correct
B network route
B network route
B. network route
What is network route ?
The correct answer is B
Network route